Jooyong Jang's Team Developed A 6DoF Head Pose Estimation Algorithm From A Single Image
- admin
- 2024-11-04
- 1854
· Jooyong Jang's Research Team (Department of Electronic Communication Engineering) Develops
6DoF Head Pose Estimation Algorithm of Human Subjects
in a Video from a Single Image
- Presented at ECCV, one of the world’s top academic
conferences in artificial intelligence -
Professor Jooyong Jang’s research team in the Department of Electronic Communication Engineering has developed an algorithm that accurately estimates the 6-degree-of-freedom (6DoF) head pose of human subjects in a video from a single image.
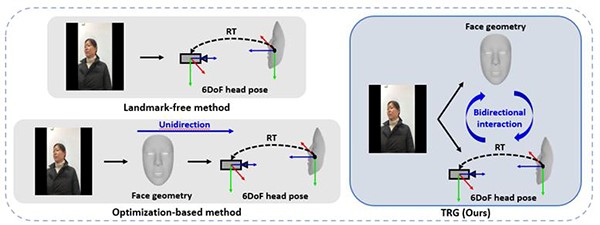
Figure 1. Comparison of existing head pose estimation
methods with the developed method (TRG)
The developed
algorithm enables the acquisition of 3D location and 3D rotation information of
the head from the image, which can be utilized in various applications such as
augmented/virtual reality, metaverse, driver monitoring systems, and
human-robot interaction. Existing methods have a unidirectional structure in
which face geometry information is first acquired and then optimized with the
image to estimate a 6Dof head pose. These methods have the drawback of being
unable to correct head pose estimation errors if the face geometry information
is inaccurately estimated. In contrast, the algorithm developed by this
research team is designed with a bidirectional structure that iteratively
refines face geometry information and head pose, overcoming the limitations of
existing methods (see Figure 1).
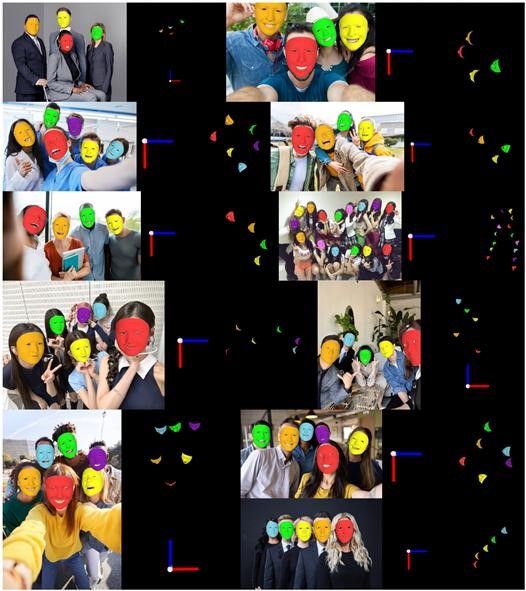

The developed
method achieved superior performance compared to existing state-of-the-art
methods on various public datasets for face geometry restoration and head pose
estimation, including ARKitFace and BIWI. Figure 2 shows examples of 6Dof head
poses obtained using the developed method on in-the-wild images containing
various human subjects.
Figure 3. PhD student Sungho Jeon presenting at ECCV
The research
was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Core Technology
Development Project for Realistic Contents (RS-2023-00219700) and Basic
Research (NRF-2022R1F1A1066170) and was presented at the European Conference on
Computer Vision (ECCV) in Milan, Italy, in early October (see Figure 3). Since
1990, ECCV has been held biennially and is regarded, alongside CVPR and ICCV,
as one of the most prestigious conferences not only in the field of computer
vision but also in the broader field of artificial intelligence. ECCV has an
H5-index of 206 on Google Scholar, making it one of the highest-ranking
international conferences in the fields of engineering and computer science. A
total of 8,585 papers were submitted to ECCV 2024, of which 2,395 were
accepted, resulting in a low acceptance rate of approximately 27.9%.
Link to paper: https://www.ecva.net/papers/eccv_2024/papers_ECCV/html/4824_ECCV_2024_paper.php