Han-Sol Choi, A Master's Student In Prof. Hyun-Ho Lee's Team, Received The IMID 2024 'Best Award.
- admin
- 2024-11-04
- 101
· Han-Sol Choi, a Master's Student in the Research Team of Professor Hyun-Ho Lee (Department of Electronic Engineering),
Han-sol Choi, a master's student in Professor Hyun-ho Lee's (Department of Electronic Engineering) research team, presented a paper titled ‘Analysis of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Damage in Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes: From Pixel to System Level’ at the 24th International Meeting on Information Display (IMID 2024), held from August 22 (Thursday) to 25 (Sunday) at the Jeju International Convention Center (ICC). The presentation earned him the 'Best Poster Paper Award.'

The International Meeting on Information Display
(IMID), jointly organized by the Society for Information Display (SID) and the
Korean Information Display Society (KIDS), has been held annually since 2001.
It is one of the world's top three international conferences for sharing the
latest knowledge in the field of information display. At IMID 2024, over 2,300
participants from 18 countries attended, with more than 950 presentations
given. Master's student Han-sol Choi received the 'Best Poster Paper Award' for
presenting a poster on the topic 'Analysis of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
Damage in Quantum Dot Light-Emitting Diodes: From Pixel to System Level.' This
research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Hyung-jun Song's
research team (Department of Safety Engineering) at Seoul National University
of Science and Technology.
Quantum dot light-emitting diodes, which utilize
quantum dots known for their high color purity and low processing cost, are
gaining attention as next-generation display devices. Inkjet printing is
emerging as an effective processing method for quantum dot light-emitting
diodes. However, there is a lack of analysis on damage caused by high voltages
that may occur during the manufacturing process, which is crucial for the
stable production of display products.
The inkjet printing process involves high voltages
from roll-to-roll, inkjet heads, and thin-film detachment, which can lead to
damage in quantum dot light-emitting diodes. By applying high voltage to the
quantum dot light-emitting diode device through electrostatic discharge, the
electrical characteristics were analyzed, observing an increase in leakage
current and impedance as well as a decrease in luminance. Optical analysis
further revealed damage to the light-emitting surface under high voltage conditions.
The damage mechanism of quantum dot light-emitting diodes caused by
electrostatic discharge was identified, with observations including phenomena
such as mixing or detachment of the anode within the device. Furthermore, it
was discovered that when high voltage is applied to one device within a quantum
dot LED panel arranged in a matrix, the same damage mechanism occurs in other
devices sharing common electrodes with the affected device.
This research was supported by the University-Focused Research Institute
and Basic Research programs (2018R1A6A1A03025242, 2022R1F1A1066526).
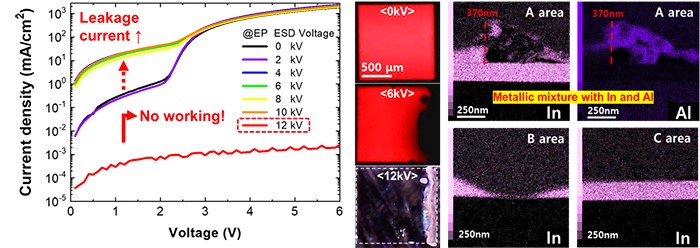
(From
left) Current density-voltage characteristic curve of quantum dot
light-emitting diodes with increasing electrostatic discharge voltage,
reduction of the light-emitting area with increasing voltage, and
energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) analysis results of damaged quantum dot
light-emitting diodes>