Prof. Jihoon Lee’s Research Team Successfully Implements an Optical Communication System
- admin
- 2024-10-23
- 125
· Professor Jihoon Lee’s Research Team (Department of Electronic Engineering) Successfully Implements an Optical Communication System
Based on 0D/2D ZnO Quantum Dots (QD)/MXene Nanosheet (NS) Composite Thin Films
- Published in the top 9.1% of JCR-ranked journals in the ENERGY & FUELS category (Q1, IF: 10.7)
- Developed a synergetic enhancement strategy for light utilization and carrier transfer for UV photodetection associated with artificial resonance nano-cavities -
Professor Jihoon Lee’s research team in the Department of Electronic Engineering from Kwangwoon University has developed a synergetic enhancement strategy for utilizing light and transferring carriers for UV photodetection associated with artificial resonance nano-cavities, successfully implementing an optical communication system based on 0D/2D ZnO quantum dots (QD)/MXene nanosheet (NS) composite thin films.
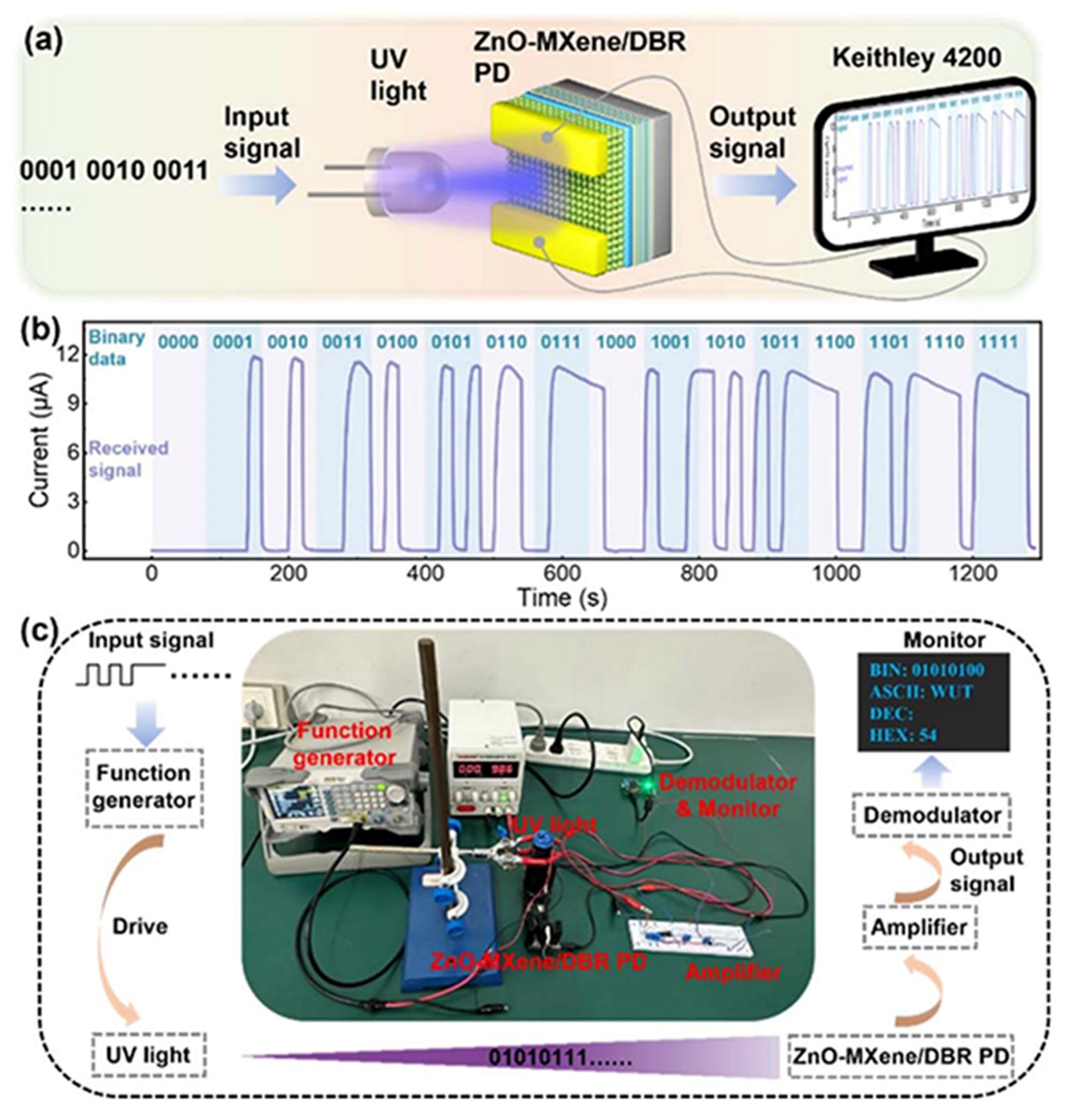
Low-dimensional wide-bandgap semiconductors show great potential for large-scale manufacturing of next-generation UV photodetectors (PDs) due to their high integration and easily tunable response spectra. However, issues such as defect density and thickness dependency on light absorption negatively affect carrier generation and transport in the photoactive layer, hindering the simultaneous realization of high sensitivity and low noise. In this study, a high-performance UV photodetector was realized by implementing an artificial resonance nano-cavity of 0D/2D ZnO QD/MXene NS composite thin films on a distributed Bragg reflector (DBR). Uniformly distributed MXene NS concentrated incident photons in the composite thin film via an enhanced near-surface electromagnetic field, accelerating the extraction and transport of photoinduced carriers, as demonstrated both experimentally and theoretically. The spatial optical coupling between MXene NS and DBR with balanced periodicity in the dielectric layers complemented the photomaterial interaction within the 0D/2D composite thin film, leading to comprehensive performance improvements. The 0D/2D ZnO QD/MXene NS composite thin film system opened a practical path for manufacturing UV photodetectors with excellent photoresponse and long-term stability.
This research was a collaborative effort involving Kwangwoon University, Wuhan University of Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology, and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China. It was supported by Kwangwoon University, the Priority Research Center, and the BK-21 project of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Ministry of Education. The research findings were published in Journal of Materials Chemistry A (JCR Q1 IF: 10.7, top 9.1% in the ENERGY & FUELS category), Volume 12, Issue 3, under the title “A synergetic enhancement strategy of light utilization and carrier transfer for UV photodetection associated with artificial resonance nano-cavities.”
* Web link: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ta06308a

Professor Jihoon Lee, Department of Electronic Engineering
Meanwhile, Professor Jihoon Lee’s research team is conducting various studies on high-efficiency, high-performance optoelectronic devices, energy devices, and system technologies based on nanomaterials and metasurfaces. To date, Professor Lee has published over 170 JCR-ranked SCI papers. He also serves as an Assistant Editor and Editorial Board member for several SCI journals of world-renowned publishers, as well as a Guest Editor for various SCI international journals. He holds multiple roles in international conference committees and organization teams. He also serves as a reviewer for over 30 SCI journals, including Advanced Materials (IF 27.4), Nano Energy (IF 16.8), and Advanced Functional Materials (IF 18.5).